Common alternative or contrast materials
-440A /440B: lower carbon content (0.75%/0.9%), slightly lower hardness but better toughness.
- S30V/S35VN: Powder metallurgy steel, corrosion resistance, toughness, but high cost.
-D2 Tool steel: higher wear resistance, but poor corrosion resistance, need plating protection.
M390/20CV: high-end powder stainless steel, the comprehensive performance is far more than 440C, the price is expensive.
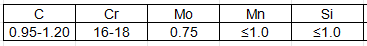
Chemiscal composition:
Heat Treatment:
The performance of 440C is highly dependent on heat treatment, typical processes:
1. Austenitizing: heating to 1010-1065°C, oil quenching or air cooling after heat preservation.
2. Temper:
- Low temperature tempering (150-370°C) : maintains high hardness (HRC 58-62), suitable for tools.
- High temperature tempering (> 480°C) : reduces hardness and improves toughness (for impact resistant parts such as bearings).
3. Cryogenic treatment (optional) : Cooling below -80°C to reduce residual austenite and improve dimensional stability.
The specialty of the steel:
Hardness: up to HRC 58-62 after heat treatment (depending on process).
- Wear resistance: Excellent, suitable for high friction environments (e.g. bearings, blades).
- Toughness: relatively low, easy to break (need reasonable design to avoid stress concentration).
Corrosion resistance: better than ordinary carbon steel, but weaker than austenitic stainless steel (such as 304/316).
- Weakness: Long-term exposure to moisture or salt spray may rust, requiring regular maintenance.
Main uses:
- Knives: high-end kitchen knives, surgical instruments, folding knives (need to be polished or coated to prevent rust).
- Bearings: precision ball bearings, valve parts (high load, wear resistance).
- Molds and machinery: plastic molds, measuring tools, wear parts.
- Aerospace: small components with specific corrosion resistance and wear resistance.
Contact: Amy Ruan
Phone: 0086-15897795404
E-mail: manager@risinmouldsteel.com
Whatsapp:0086-15897795404
Add: Sanyuan Road, Xisai Mountain Industrial Park, Huangshi City, Hubei Province
We chat